IMO Approvaled Ballast Water Treatment System
1.Treatment Technology of ballast water treatment system
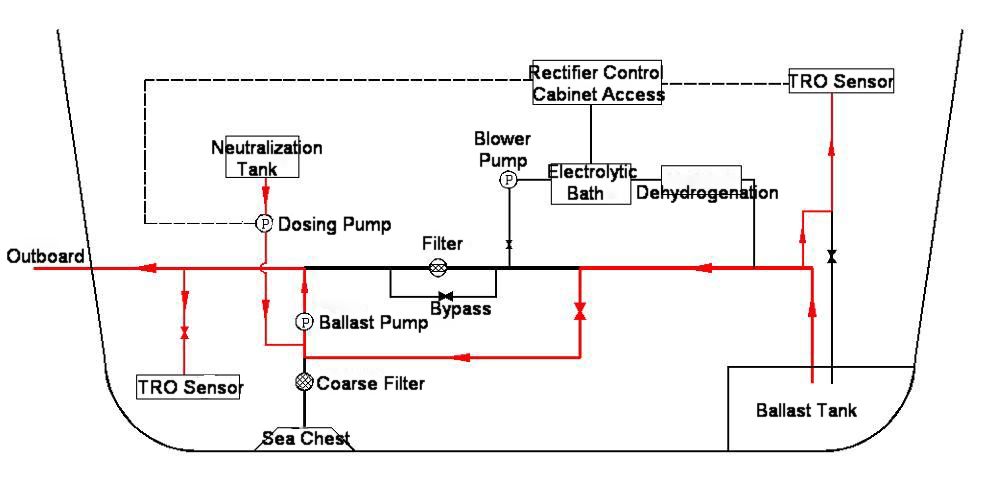
The treating process of ballast water treatment system is mainly consisted of the following three procedures:Filtration ---The ballast water is filtrated by an automatic backwashing filter with 50µm screen to remove marine organisms larger than 50µm.
Disinfection --- A small side stream of the filtered ballast water is delivered to the electrolytic unit to generate the oxidants of high concentration (mainly sodium hypochlorite solution), then the oxidants are injected back into the main ballast stream to provide effective disinfection.
Sodium hypochlorite solution as a very effective germicide can be kept in ballast water for a certain period to effectively kill the plankton, spores, larvae and pathogens contained in the ballast water to meet D-2 standard.
Neutralization --- The residual TRO level of the treated ballast water below 0.1ppm, then the treated ballast water can be directly discharged. If the residual TRO level of the treated ballast water over 0.1ppm, neutralizer (sodium thiosulfate solution) is added into the de-ballast pipe to neutralize residual oxidants instantly automatically.
2. Disinfection principle——Core technology
When seawater flows through the electrolyzer, decomposition reactions take place on the electrode surfaces, with chlorine produced at the anode and hydrogen gas at the cathode.The reaction principle is as follows:
Anode: 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e
Cathode: 2H2O + 2e → 2OH- + H2↑
Chlorine gas can be dissolved in water to produce hypochlorous acid and hydrochloric acid rapidly:
Cl2 + H2O → HOCl + Cl- + H+
So the whole reaction is:
NaCl + H2O → NaOCl + H2↑
Sodium hypochlorite solution as a very effective germicide can be kept in ballast water for a certain period to effectively kill the plankton, spores, larvae and pathogens contained in the ballast water. This technology has been widely practiced in water treatment industries like medical sterilization, water treatment fields for many years.
3. BWMS Working Process
4. Specification
|
Model |
Treatment Capacity |
Flow Rate to Electrolyzer |
Required Power |
Dimension |
|
|
Filter (mm) |
Electrolysis Unit (mm) |
||||
|
(m3/h) |
(m3/h) |
(AC KVA) |
L×W×H |
L×W×H |
|
|
BC-300 |
100-300 |
6 |
15 |
3000×600×800 |
2500×1800×2200 |
|
BC-500 |
301-500 |
6 |
25 |
3300×600×800 |
2600×1800×2300 |
|
BC-1000 |
501-1000 |
12 |
50 |
3300×600×800 |
2900×2300×2200 |
|
BC-1500 |
1001-1500 |
20 |
75 |
3400×800×1070 |
3000×2600×2100 |
|
BC -2000 |
1501-2000 |
20 |
100 |
3300×1500×800 |
3300×2500×2200 |
|
BC -2500 |
2001-2500 |
36 |
125 |
3400×1800×1070 |
3500×2900×2400 |
|
BC -3000 |
2501-3000 |
36 |
150 |
3400×1800×1070 |
3500×2900×2400 |
|
BC -3500 |
3001-3500 |
36 |
175 |
3400×1800×1070 |
3800×2400×2500 |
|
BC -4000 |
3501-4000 |
36 |
200 |
3500×3300×770 |
3800×2400×2600 |
|
BC -5000 |
4001-5000 |
45 |
250 |
3500×3600×770 |
4000×2800×2600 |
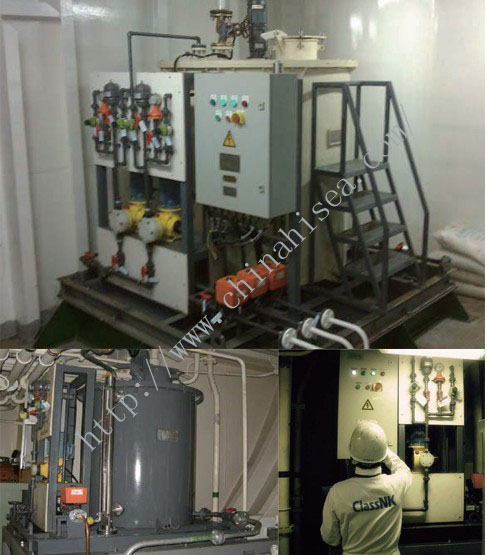
5. Electrolysis Unit

6. Neutralization Unit

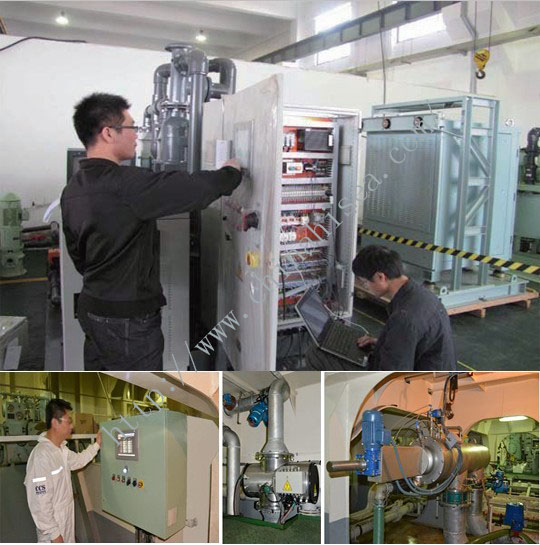
7. Unit Testing

8. Certificate
Society certificates






CONTACT WITH US NOW